Picture 47

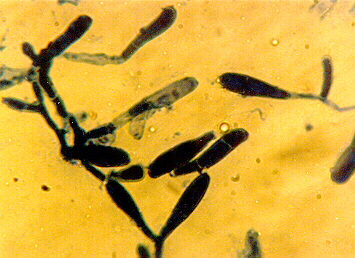
This picture shows Epidermophyton floccosum.
Epidermophyton floccosum
Morphology: Microconidia are are never formed. Macroconidia are numerous, clubbed-shaped with slightly rough walls. Colonies grown on Sabouraud's Dextrose Agar (SDA) show a powdery surface. It has an olive green colour with radiating furrows. Tufts of white floccose growth appear on the surface.
Route of transmission: Direct contact
Investigations: KOH smear and culture from skin scrapings, discoloured hairs and kerototic debris
Diseases:
Infects, grows and remains confined to keratinous structures in the body.
1. Foot infection (Athlete's foot, tinea pedis), the hands are less commonly infected
2. Scalp infection (tinea capitis), can sometimes lead to an intense baggy suppuration known as a kerion
3. Nail infection (onychomycosis, tinea unguium) presents as white, discoloured nails or chalky, crumbling nails
Treatment:
Topical antifungals, eg. clotrimazole, miconazole, or ketoconazole for mild infections.
Systemic griseofulvin for more severe or unresponsive cases.
Oral ketoconazole for cases unresponsive to griseofulvin.
Next Picture