Picture 34

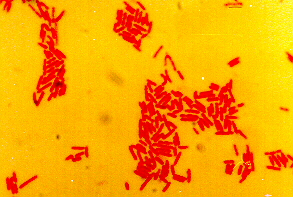
This picture shows a Gram stain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Morphology: Gram negative rods, do not ferment glucose and lactose, are oxidase positive, produce pyocyanin and pyoverdin
Route of transmission: Fomites and food
Investigations: Gram stain, culture in MacConkey's agar or Triple Sugar Iron medium
Diseases:
Pneumonia
Urinary tract infection
Wound infection
Septicemia
Meningitis
Otitis externa
Endophthalmitis
Osteomyelitis
Treatment:
Due to varied antibiotic resistance, choices for empirical treatment include the aminoglycosides (eg. gentamicin and tobramycin), some third generation cephalosporins (eg. ceftazidime and cefoperazone), extended spectrum penicillins (eg. piperacillin, azlocillin and carbenicillin), carbapenems (eg. imipenem and meropenem), and fluoroquinolones (eg. ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin) until results of sensitivity tests are known.