Picture 5

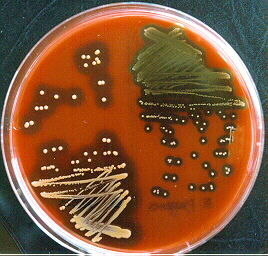
This picture shows Staphylococcus aureus (lower left quadrant), and Streptococcus pyogenes (upper right quadrant) in blood agar.
Staphylococcus aureus
Morphology: colonies golden yellow in colour, Gram positive cocci arranged in 'grapelike' clusters, beta-hemolytic, coagulase positive, catalase positive
Route of transmission: fomites
Investigations: Gram stain and culture
Diseases:
Superficial skin infections, eg. folliculitis, furuncle
Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome especially in infants and children
Septicemia and endocarditis
Pneumonia
Treatment: Vancomycin (for MRSA), Cloxacillin and Flucloxacillin (for non-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
Streptococcus pyogenes
Morphology: colonies are white and shiny, Gram positive cocci arranged in chains or pairs, beta-hemolytic, catalase negative
Route of transmission: fomites
Investigations: Gram stain and culture, Anti-Streptolysin O titers
Diseases:
Pharyngitis (may cause post infectious acute rheumatic fever and glomerulonephritis)
Impetigo
Cellulitis and necrotizing fasciitis
Treatment:
Penicillin V for minor infections
IV Benzylpenicillin G for major infections
IM Benzathine penicillin G for prophylaxis of rheumatic fever
Surgical debridement in necrotizing fasciitis