Development and growth, state of nutrition
Development and growth
- Gigantism
- Nanism
State of nutrition
- Obesity
- Cachexia
The development
and growth of a human organism runs proportionally,
under the influence of hormonal, mental, metabolic, and genetic factors.
The average height varies. High or low build can be considered normal
if occurs in family.
Gigantism
means an exceedingly high build. The development of the individual
is proportional, but acromegalic features can also be developed (prominent
supraorbital arcs, nose, chin). It is caused by hypersecretion of somatotropin
in childhood, before the closure of growth plates.
Eunuchoid
growt
is characterised by a higher build with disproportion between the length
of the extremities and the trunk, which is relatively shorter.
Praepubertal hypogonadism is causing this condition.
Dwarfism
means a proportional small build. The limit of the height for men is 145 cm, for women 135 cm. This occurs in case of hormonal, genetic chromosomal defects (Turner syndrome, ovarian dysgenesis) or in case of congenital metabolic disorder.
The state of nutrition
Can be tentatively told from the first glimpse. BMI, subcutaneous fat measuring
and Brock's formula can be used as objective assessment:

Face of an
acromegalic
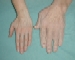
Hands of an
acromegalic
![]()
Legs of an
acromegalic
Obesity
Primary (simple) obesity is caused by excessive energetic supply in comparison to the output.
Secondary obesity is less common, it accompanies other diseases (e.g. endocrine).
It is represented by an excessive accumulation of the subcutaneous fat, especially on the trunk.

Diffuse
obesity is usually congenital, caused by a genetic or hormonal abnormality
(defect of hypothalamus). It also includes Fröhlich
(adiposogenital) syndrome (obesity and hypogonadism). The fat
accumulates in the trunk and upper and lower extremities.

Truncal obesity is usually related to the excessive food intake. It is often combined with metabolic, hormonal, and other defects. The fat is accumulated in the trunk.
Cushing syndrome develops in
case of hypercorticoidism. The fat is accumulated in the face,
which gains a moon appearance (moon face), behind the neck, between
the shoulder blades, and on the abdomen, where violet
striae develop.
Pickwick syndrome is a term
used to describe obese patients with chronic respiratory insufficiency.
The main symptoms are inversion of sleep, central cyanosis, and polyglobulia.
Cachexia
is caused by absence of the fat deposits and muscular atrophy. It is manifested
by extreme skinniness.
Cachexia may be caused by:

tumours of gastrointestinal tract, and some inflammations (tuberculosis),

hypopituitarism (Simmonds´ cachexia, Sheehan syndrome)

active thyrotoxicosis

Addison's disease

mental anorexia
Progressive lipodystrophy occurs in girls by a disproportional storage of fat in the lower part of the trunk, while in the upper part the fat vanishes.
Necrobiosis – diabetic lipodystrophy is characterised by a local
loss of fat in association with insulin administration.
Your notes, observations, and proposals are welcome either via e-mail at the address

Obesity,
phlebo-thrombosis
of the left arm

Obesity,
monstrous
ventral hernia

Cushingoid
face
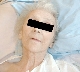
Anaemia,
senile
cachexia
